New science shows that a single brief computerized cognitive assessment—Double Decision from BrainHQ – can predict brain levels of acetylcholine—an important measure of brain health.
What is acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine is a molecule made in the brain that acts as a neuromodulator—a chemical that controls the overall health and function of the brain. There are a lot of neuromodulators, including serotonin (which is involved in mood and depression) and dopamine (which is involved in how the brain processes rewards, as well as addiction)
Why is acetylcholine important for brain health?
Acetylcholine is an important neuromodulator because it is involved in attention and brain plasticity. When you pay attention to something, your brain releases acetylcholine. This tells your brain that something important is going on—and it enables your brain to rewire itself (a process known as brain plasticity) to learn and remember what happened.
Acetylcholine is produced in a part of the brain called the basal forebrain. Doctors have known for a long time that an early symptom of the onset of Alzheimer’s disease is a decline in the function of the basal forebrain and a decline in the amount of acetylcholine available in the brain. This is related to the problems that people with Alzheimer’s disease have with attention, learning, and memory—and is likely related to overall decline in brain health. We know acetylcholine is important in Alzheimer’s disease because some of the first medications that helped—just a bit—with Alzheimer’s disease were medications that helped maintain brain levels of acetylcholine.
What did the study show?
The INHANCE (Improving Neurological Health in Aging via Neuroplasticity-based Computerized Exercise) study showed that a simple computerized cognitive assessment—Double Decision, part of the BrainHQ brain health program—can predict the level of acetylcholine in the brain in people 65 and older who did not have dementia, and in this way, is a measure of overall brain health. Double Decision is a well-established assessment that measures brain speed and attention, so it makes sense that it also can measure brain acetylcholine levels. This is a breakthrough result, because it is very difficult to measure brain acetylcholine levels in ordinary medical practice—it requires the use of advanced brain imaging systems and the use of a slightly radioactive chemical. As a result, doctors have to diagnose brain health conditions without any knowledge about the health and function of the brain’s acetylcholine levels—even in conditions where those acetylcholine levels may be contributing to the brain health condition.
Where acetylcholine is found in the brain
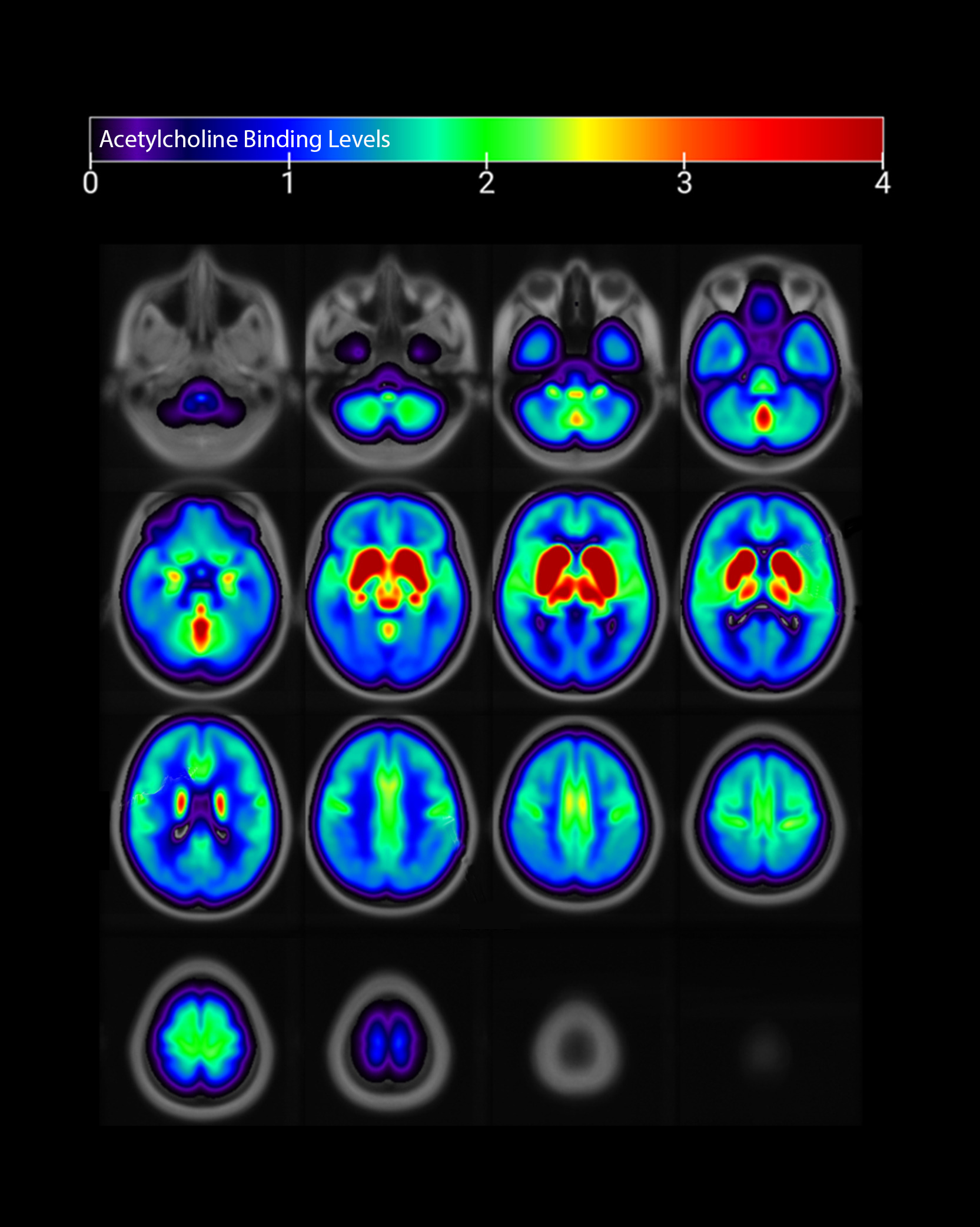
Do we know what a “healthy” or “good” level of acetylcholine is?
The science is still early, and so it’s not possible yet to say definitively what a “healthy” or “good” level of acetylcholine is. In this study, the average level of acetylcholine was 1.90 (corresponding to a Double Decision score of 1477 milliseconds), and people who were at risk for cognitive decline typically had acetylcholine levels of 1.49-1.88 (corresponding to Double Decision scores of 1800-3164 milliseconds, note that lower Double Decision scores are better).
The Double Decision assessment is not a medical test, and you should not rely on your test results for making a medical decision. We are presenting the test as a demonstration for people who are curious about the new study results and want to learn more about how the study was conducted.

Can I improve my brain health and brain acetylcholine levels?
Hundreds of scientific publications now show that you can improve your brain health, cognitive performance, and real-world function with BrainHQ training. Give it a try!
How about improving acetylcholine levels specifically? The INHANCE study also looked at the effects of BrainHQ training on brain acetylcholine levels. Stay tuned for upcoming news about that exciting result! Sign up for the BrainHQ newsletter to stay up to date on this and other exciting brain health news!
